Create Custom Triggers



In this guide we will explore how you can create a custom trigger for your AutoPi service. The example that we will look at is a trigger that will play a beeping sound when the vehicle's speed is 50km/h or more. Let's dive straight in.
Service triggers are not to be confused with Cloud triggers. Although they have the same name they have two very different functions. Service triggers work on the device and can respond to data coming in from a handler in various ways (emiting events, playing audio, etc). Cloud trigers on the other hand respond to events emited by the device on the server side.
- Let's start by creating a custom code module with the name my_triggers of type Execution. We can do that by going over to Device > Custom Code:
Here is the code in plain text for easy copy and paste:
import logging
from messaging import extract_error_from
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def speed_warning_beep(result):
"""
Trigger that will play a warning beep sound when vehicle speed exceeds value of 50.
"""
# Check for error result
error = extract_error_from(result)
if error:
log.warning("Speed warning beep trigger got error result: {:}".format(result))
return
# Check if speed value is above threshold
if result.get("value", 0) >= 50:
# Only play sound when threshold value is exceeded
if not __context__.get("speed_warning_beep", False):
__salt__["cmd.run"]("aplay /opt/autopi/audio/sound/beep.wav")
# Set flag in context
__context__["speed_warning_beep"] = True
# Speed value is below threshold
else:
# Reset flag in context
__context__["speed_warning_beep"] = False
To quickly run through the code, this code creates a function that will check if the result
passed to it has a value key that is equal to or more than 50. Once that condition is met, it
will make sure that the vehicle isn't already in that state through the context (if the vehicle
is continuously above 50km/h we won't play the beeping sound continuously) and if it isn't it'll
play the beeping sound. Once the above or equal to condition is no longer met, we reset the
context.
Now, let's synchronise the changes to the device by clicking the Sync button. If the device is offline the changes will automatically be synchronised on next start-up.
- Next, we need to register that trigger in the service that it'll be used. For this guide, we need to register it in the OBD service named obd_manager. Go to Device > Services > obd_manager > Hooks > Create:
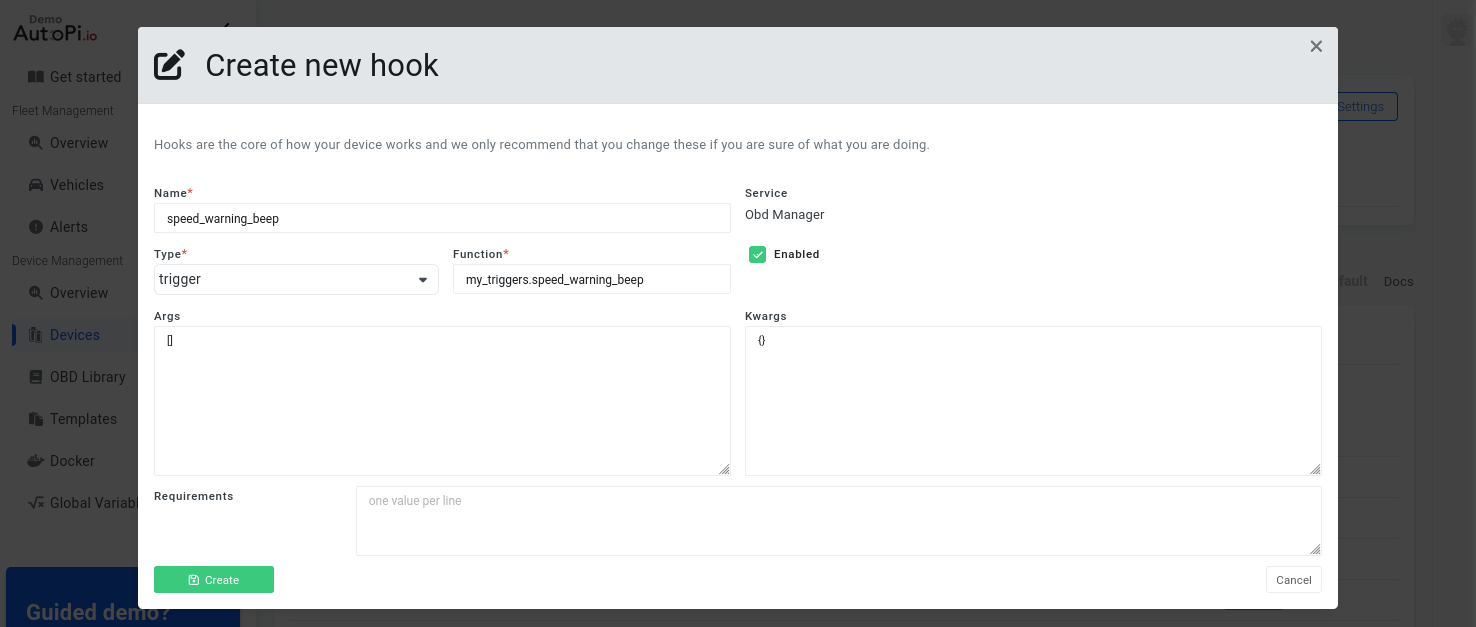
- We now need to use the newly registered trigger hook by adding it to a workflow in a worker. Go to Device > Services > obd_manager > Workers > Create:
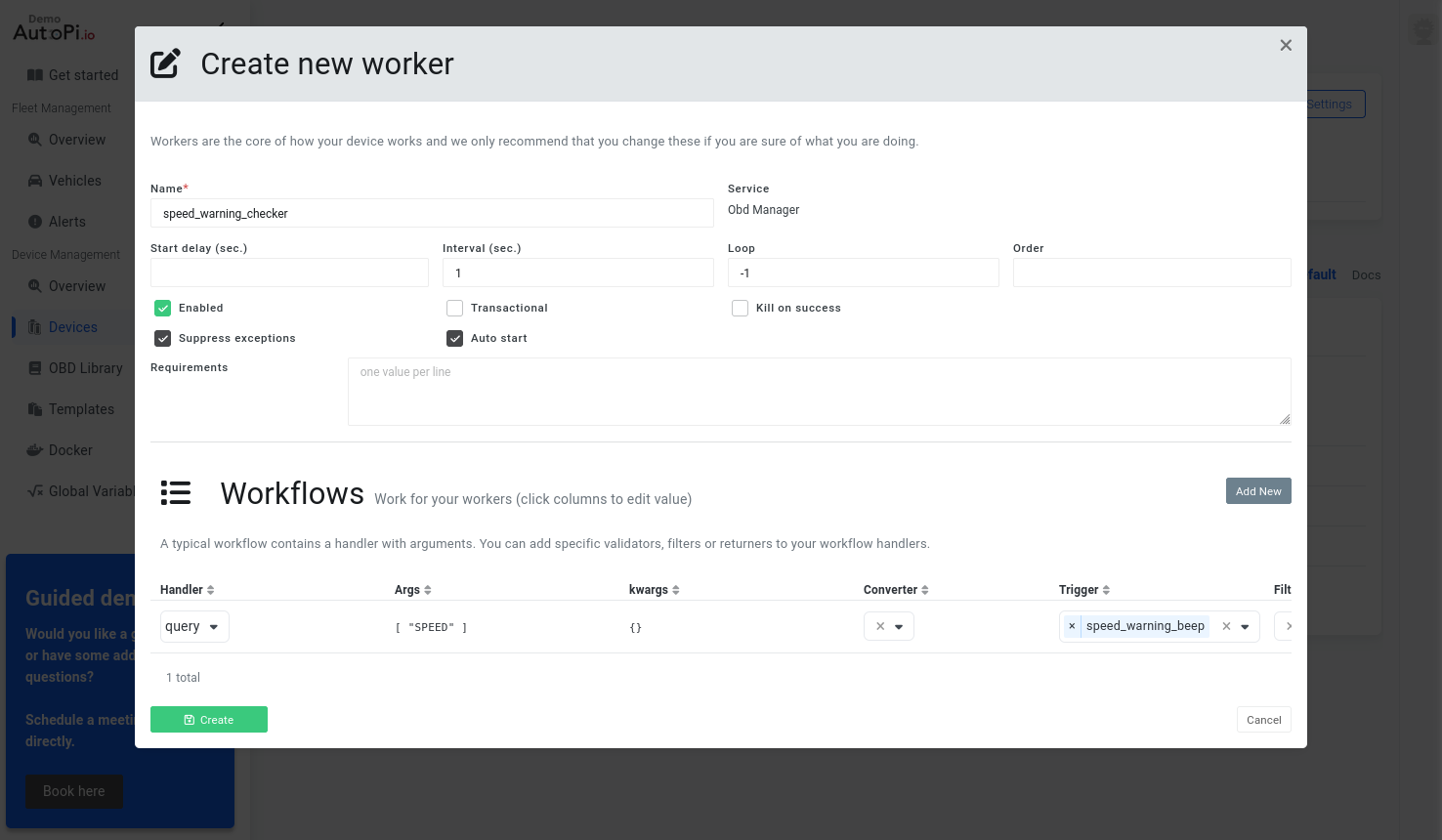
When the above changes have been successfully synchronised to your device, it will start checking the speed of your vehicle and play a single beep sound when exceeding 50km/h.
The query handler with a SPEED argument is only valid for some vehicles, mostly internal
combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. If you have an electric vehicle, you might need to use a more
sophisticated setup to get the current speed of your vehicle. We suggest that you browse forums
for your make and model for such information.
Check the log file on the device to see if there are warnings and/or errors. Check this guide out for more information on how to retrieve the logs from your device.
Want an Event Instead of a Beep?
You can freely fire events from your custom code modules. If you're looking to execute one or multiple different actions based on some event (in this case, speeding over 50km/h), you are able to do that. Let's add another function to the my_triggers custom code:
def speed_warning_event(result):
"""
Trigger that will fire a 'vehicle/speeding' event when vehicle speed exceeds value of 50.
"""
# Check for error result
error = extract_error_from(result)
if error:
log.warning("Speed warning event trigger got error result: {:}".format(result))
return
# Check if speed value is above threshold
if result.get("value", 0) >= 50:
# Only play sound when threshold value is exceeded
if not __context__.get("speed_warning_event", False):
__salt__["event.fire"]({}, "vehicle/speeding")
# Set flag in context
__context__["speed_warning_event"] = True
# Speed value is below threshold
else:
# Reset flag in context
__context__["speed_warning_event"] = False
The code here is esentially the same as the one presented above. The only difference is that the AutoPi will fire an event internally instead of playing a beeping sound. This event can then be used in the event_reactor service to perform other actions. Also, the event will be uploaded to the Cloud and be visible from Device > Events.
 Buy AutoPi device
Buy AutoPi device Compare all AutoPi devices
Compare all AutoPi devices