Accessing Raw GPS Data (10 Hz)



This guide explains how to enable and stream raw GPS (NMEA) data at 10 Hz from your AutoPi device.
Overview
By default, the device’s GNSS Manager service handles GPS communication. To stream raw NMEA data directly, this service must first be disabled to free up the serial (TTY) port used for GPS communication.
Once disabled, you can use a simple Python script mentioned below to configure the GPS polling rate, enable streaming mode, and read data from the serial output in real time.
Steps
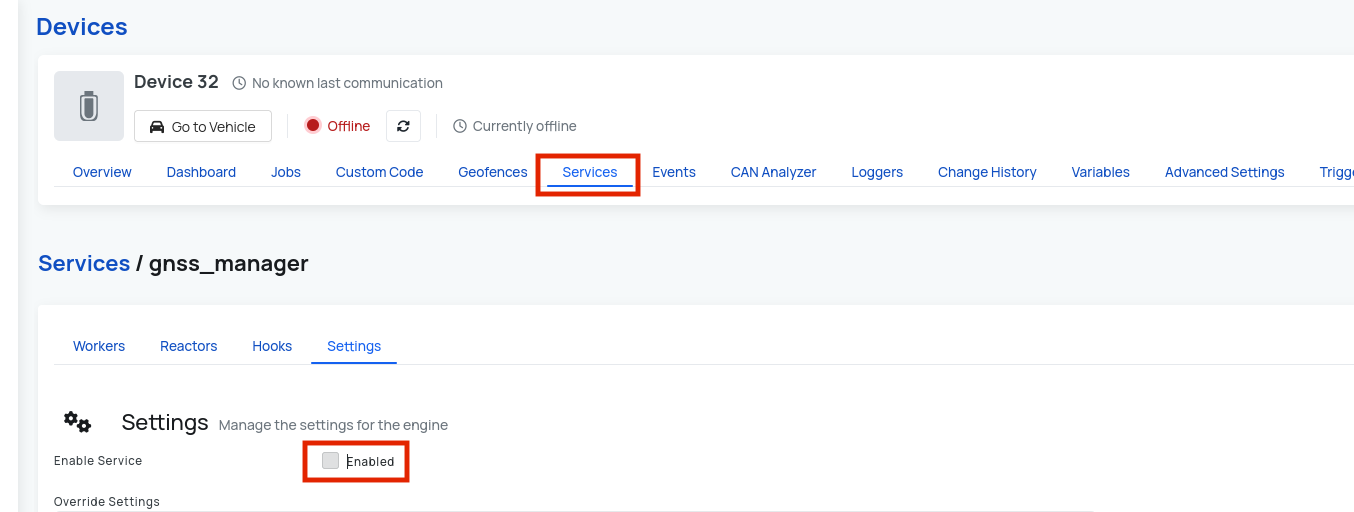
1. Disable the GNSS Manager Service
- Navigate to the device you want to configure on AutoPi's cloud
- Go to Services page under Device.
- Locate the
gnss_managerservice. - Disable the service. Disabling this service ensures that no other process is using the same TTY port needed for raw NMEA streaming.
2. Configure and Start the GPS Data Stream
Use the provided Python script to set up the GPS polling rate and start the NMEA data stream.
This example script:
- Configures the GPS to output data at 10 Hz
- Enables continuous streaming mode
- Prints raw NMEA sentences to stdout
You can modify the script to log data to a file, filter specific NMEA messages, or integrate with your application.
You can copy the example Python script below:
#!/bin/python3
import serial
import time
import threading
PORT_GPS = "/dev/ttyTLT02"
PORT_MODEM = "/dev/ttyTLT01"
BAUD = 115200
stop_flag = False
def key_listener():
global stop_flag
key = str(input())
print("you pressed {}".format(key))
stop_flag=True
def setup_gps():
with serial.Serial(PORT_GPS, BAUD, timeout=1) as modem:
modem.reset_input_buffer()
modem.reset_output_buffer()
modem.write(b'AT$GPSNHZ?\r')
time.sleep(0.5)
response = modem.read_all().decode(errors="ignore")
if not "3" in response:
modem.write(b'AT$GPSP=0\r')
time.sleep(5)
modem.write(b'AT$GPSNHZ=3\r')
time.sleep(5)
modem.write(b'AT$GPSP=1\r')
time.sleep(5)
# open port!
modem.write(b'AT$GPSNMUN=2,1,0,0,0,0,0\r')
time.sleep(5)
def stop_streaming():
with serial.Serial(PORT_GPS, BAUD, timeout=1) as modem:
modem.reset_input_buffer()
modem.reset_output_buffer()
modem.write(b'AT$GPSNMUN=0\r')
time.sleep(0.5)
return modem.read_all().decode(errors="ignore")
def run():
global stop_flag
consecutive_errors = 0
while not stop_flag:
try:
setup_gps()
with serial.Serial(PORT_GPS, BAUD, timeout=0.1) as ser:
print("Listening for NMEA...")
while not stop_flag:
try:
line = ser.readline().decode(errors="ignore").strip()
if not line:
consecutive_errors += 1
if consecutive_errors > 10:
print("Too many consecutive errors, assuming disconnect.")
break
continue
consecutive_errors = 0
if line.startswith("$"):
print(line)
if stop_flag:
print("EXITING NOW!!!")
except serial.SerialException as e:
consecutive_errors += 1
print("Serial error: {}".format(e))
except Exception as e:
print("Unexpected error: {}".format(e))
except serial.SerialException as e:
consecutive_errors += 1
print("Could not open serial port {}: {}".format(PORT_GPS, e))
except Exception as e:
print("General error: {}".format(e))
res = stop_streaming()
print("stopped streaming with res: {}".format(res))
if __name__ == "__main__":
n=threading.Thread(target=key_listener).start()
i=threading.Thread(target=run).start()
3. Verify Data Stream
When the script runs successfully, you’ll see a continuous stream of raw NMEA sentences, for example:
$GPGGA,120000.00,5540.1234,N,01234.5678,E,1,12,0.8,15.0,M,40.0,M,,*5C
$GPRMC,120000.00,A,5540.1234,N,01234.5678,E,0.13,240.15,060625,,,A*6D
These sentences contain the raw GPS position, velocity, and time data updated at 10 Hz.
Troubleshooting
While configuring your AutoPi device to be able to stream GPS data at 10 Hz, some issues may arise and therefore we are mentioning the most common issues and ways to solve them.
GPS Port Not Found
If you receive an error such as:
serial.serialutil.SerialException: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/dev/ttyUSB0'
- Run dmesg | grep tty on the device to list available serial ports.
- The GPS may appear as /dev/ttyS4, /dev/ttyACM0, or /dev/ttyUSB1 depending on your setup.
- Update the tty_device variable in the script accordingly.
Permission Denied
If you see a permission error when opening the serial port:
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: '/dev/ttyS4'
- Run the script as root or add your user to the dialout group:
sudo usermod -a -G dialout $USER
Then log out and back in.
No Data Received
If the script runs but no NMEA data is printed:
- Confirm that the
gnss_managerservice is disabled. - Check that your GPS module has a valid satellite fix (usually indicated by an LED or diagnostic message).
- Try reducing the baud rate (e.g., 9600) if unsure of the GPS module’s settings.
 Buy AutoPi device
Buy AutoPi device Compare all AutoPi devices
Compare all AutoPi devices